In vivo, ex vivo, and in vitro investigations on animals are used in non-clinical pharmacokinetic (PK) studies to understand the processes and properties of drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, as well as to disclose the dynamic changes of pharmaceuticals in vivo. Non-clinical PK studies are crucial to the evaluation of novel drug development research.
To assist the IND phase of a candidate molecule, Our company provides a comprehensive preclinical PK study solution. We have a dedicated PK team to give expert interpretation and solutions for additional preclinical safety assessments for the generated results and data.
We have listed our specific solutions below.
In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Studies
- Animal species: Mice, rats, rabbits, dogs, crab-eating monkeys, rhesus monkeys, small pigs, etc.
- Route of administration: Intravenous, oral, subcutaneous, intraperitoneal, intramuscular, local administration, etc.
- Biological substrate collection: Whole blood, plasma, serum, urine and feces, bile, cerebrospinal fluid, various tissues, etc.
- Microsampling: One mouse, one PK profile.
- Detection methods: LC-MS, MS, LC-QTOF, RT-PCR, ELISA, radioisotope labeling, etc.
- Data analysis: We perform PK, pharmacodynamics (PD), and physiologically based PK modeling (PBPK) calculations and simulations by Phoenix WinNonlin and Gastrol plus.
- Specialty services: Non-clinical PK studies of radioisotope-labeled compounds.
Drug Interaction Studies
- Inhibition experiments: 1. Reversible inhibition. 2. Time-dependent inhibition.
- Metabolic phenotype assay: 1. Cytochrome P450 (CYP), chemical inhibition assay and recombinant enzyme assay. 2. UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT), recombinant enzyme assay.
- Enzyme induction assay: CYP450 enzyme isoforms.
- Transporter assays:
1. ABC-like transporter substrate assays (P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein). Vesicular system or Caco-2 cells.
2. ABC-like transporter substrate inhibition assay (P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein). Vesicular system.
3. SLC-like transporter substrate assay (OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OAT1, OAT3, OCT2, MATE1, MATE2K).
4. SLC-like transporter inhibition assay (OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OAT1, OAT3, OCT2, MATE1, MATE2K).
Drug Excretion Studies
- Using mouse/rat metabolic cages, urine and feces excreted by mice and rats in their natural state were collected and analyzed by performing LC-MS and MS.
- Bile ducts were cannulated in rats, and bile was collected and analyzed by performing LC-MS and MS.
- After using 3H and 14C radioisotope-labeled drugs, the radioactivity of feces, urine and bile of experimental animals was measured (Online monitoring of radioactivity - HPLC-mass spectrometry).
- The total radioactivity of feces, urine, and bile of experimental animals was measured after using 125I-labeled drugs.
Drug Metabolism Studies
- Metabolic stability studies: Hepatocytes, liver S9, and liver microsomes.
- Metabolite identification tests (microsomes/hepatocytes/whole animals).
- CYP enzyme phenotyping/enzyme inhibition/enzyme induction studies.
- Metabolite analysis after using 3H, 14C labeled compounds drug.
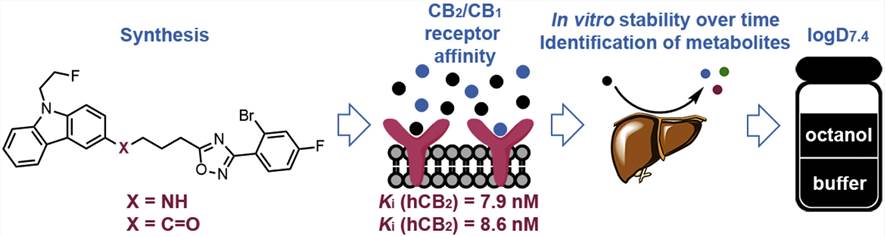 Fig.1 The metabolic stability study of a fluorinated cannabinoid receptor subtype 2 (CB2) ligand. (Heimann D, et al. 2018)
Fig.1 The metabolic stability study of a fluorinated cannabinoid receptor subtype 2 (CB2) ligand. (Heimann D, et al. 2018)
Drug Distribution Studies
- Multiple genus tissue distribution measurements.
- The ability of the subjects to cross the blood-brain barrier into the brain was investigated (Brain, Blood Ratio).
- Whole blood plasma partition ratio assay.
- Multi-generic plasma/tissue protein binding: equilibrium dialysis method, ultrafiltration membrane method.
- Determination of total and precipitated radioactivity in tissues after drug administration using 125I-labeled macromolecules.
- Determination of radioactivity in tissues after administration of small molecule drugs using 3H and 14C labeling.
Drug Absorption Studies
- Absorption assessment of single or repeated doses.
- Absorption assessment of non-rodent double cross and Latin formula design administration.
- PK-pharmacodynamic studies of biological products.
- Cell penetration studies: Cell penetration studies are based on Caco-2 cells or Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells.
Toxicokinetic Evaluation
- Repeated administration toxicity with toxicokinetic test (API or toxic component exposure).
- Reproductive toxicity with toxicokinetics (rat segment l, ll and ll, rabbit segment II).
- Concomitant biodistribution tests.
If you are looking for the best solution in the field of PK studies of drugs for human use, please feel free to contact us.
Reference
- Heimann D, et al. (2018). "Optimization of The Metabolic Stability of a Fluorinated Cannabinoid Receptor Subtype 2 (CB2) ligand Designed for PET Studies." European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 146: 409-422.
Related Services
It should be noted that our service is only used for research, not for clinical use.


 Fig.1 The metabolic stability study of a fluorinated cannabinoid receptor subtype 2 (CB2) ligand. (Heimann D, et al. 2018)
Fig.1 The metabolic stability study of a fluorinated cannabinoid receptor subtype 2 (CB2) ligand. (Heimann D, et al. 2018)